Understand Your Gut Microbiome with the Experts in GA
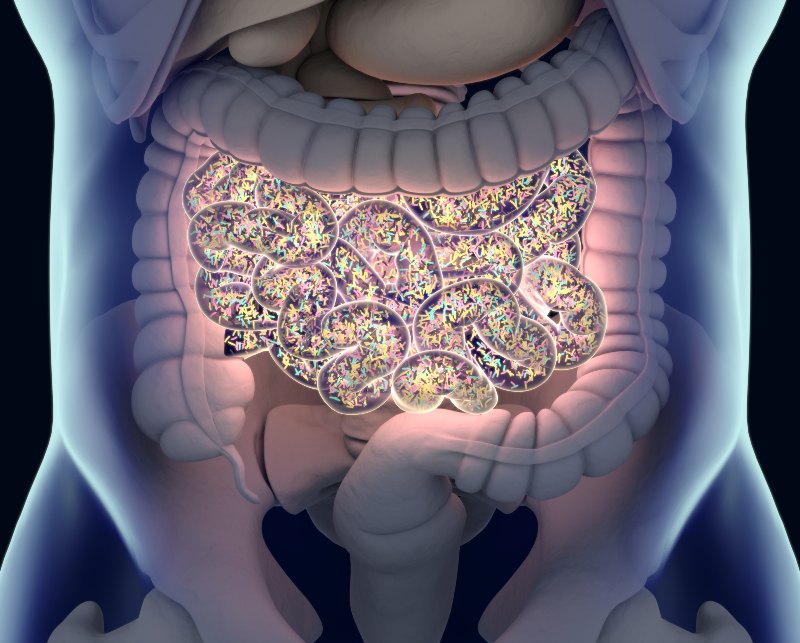
What are Microbiome and Probiotics?
The microbiome refers to trillions of microorganisms residing in your gut, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microbes. This diverse ecosystem plays a pivotal role in your overall health, influencing digestion, immunity, and even mental well-being.
Probiotics, on the other hand, are live beneficial bacteria or yeasts that you can consume through certain foods and supplements. These friendly bacteria are essential in supporting a balanced gut microbiome. Probiotics offer numerous benefits for digestive health and the rest of your body.
The Role of the Microbiome
Your gut microbiome is an incredibly dynamic environment that influences your digestive health significantly. It helps break down food, absorb nutrients, and produce essential vitamins. A healthy microbiome acts as a barrier against harmful bacteria and pathogens, reducing the risk of infections. It also communicates with the immune system, ensuring your body responds appropriately to potential threats.
Disruptions to the microbiome can lead to gut microbiome diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and other digestive issues. Therefore, understanding what gut microbiome is and maintaining its balance is vital for good health. Our GI services can help you with this.
Benefits of Probiotics
Probiotics offer many health benefits by enhancing the composition of your gut microbiome. Some key probiotic health benefits include:
- Improved Digestion – Probiotics aid in breaking down food more efficiently, alleviating symptoms like bloating and constipation.
- Enhanced Immune Function – By promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria, probiotics support your immune system's ability to fight infections.
- Alleviation of GI Disorders – Studies have shown that probiotics can help manage symptoms of IBS and reduce the severity of IBD flare-ups.
- Better Mental Health – The gut-brain axis indicates that a healthy gut microbiome can positively impact mood and cognitive functions.
Sources of Probiotics
Probiotics can be found in various foods and supplements. Fermented foods are particularly rich in these beneficial bacteria. Some excellent sources include:
- Yogurt – A well-known probiotic-rich food that can improve gut health.
- Kefir – A fermented milk drink packed with diverse probiotic strains.
- Sauerkraut and Kimchi – Fermented vegetables that offer a robust mix of probiotics and fiber.
- Miso and Tempeh – Fermented soy products that are not only rich in probiotics but also protein.
- Probiotic Supplements – Available in pill, powder, or liquid form, these supplements provide concentrated doses of beneficial bacteria.
How to Maintain a Healthy Microbiome
- Eat a Diverse Diet – Consuming a variety of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains ensures a wide range of nutrients that promote a healthy microbiome.
- Limit Antibiotics – While necessary at times, antibiotics can disrupt the balance of your gut bacteria, so they should be used judiciously.
- Stay Active – Regular physical activity can positively affect gut microbiome diversity.
- Manage Stress – Chronic stress can negatively impact your gut health, so incorporating stress-reducing activities can be beneficial.
- Stay Hydrated – Drinking plenty of water supports the mucosal lining of the intestines, promoting a healthy microbiome.
Why Choose GI Specialists of Georgia?
Contact Us Today in Atlanta, GA
If you are interested in learning more about how the gut microbiome and probiotics can benefit your digestive health, or if you're seeking effective gut microbiome disease treatment, reach out to GI Specialists of Georgia. Our experienced team is ready to guide you on your journey to better health.
Don't wait to take charge of your digestive health. Contact us today to schedule a consultation and discover how we can support your gut health, digestion & microbiome support needs. Your well-being is our priority, and we are dedicated to helping you achieve optimal digestive health.
Explore our services and take the first step toward a healthier you.
What is Esophageal Cancer?
Learn More about Esophageal Cancer
Esophageal cancer staging is important for planning treatment. Endoscopic ultrasound, CT scan, and PET/CT scan are used in the staging process.
Esophageal cancer stages include:
- Stage in situ. Cancerous cells involving the lining of the esophagus and have not invaded the deeper parts of the inner lining of the esophagus.
- Stage I. Cancer starts in the superficial layers and invades the first layers of the inner lining of the esophagus and may have spread to the lymph nodes nearby
- Stage II. Cancer has invaded deeper muscular layers of the esophagus and may have spread to the lymph nodes nearby.
- Stage III. Cancer has spread to the deepest layers of the wall of the esophagus and invades into the tissues and/or lymph nodes nearby.
- Stage IV. Cancer has spread to other parts of your body.
Treatment is multimodality depending on the staging of cancer. Treatment involves surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
If the cancer is small and limited to the superficial layers and has no evidence of spread, it can be removed via endoscopic surgery. Surgery may include partial or complete removal of the esophagus called esophagectomy. Occasionally surgery may also include partial removal of the upper end of the stomach along with the esophagus and is called esophagogastrectomy.
Drug treatment using medications to kill cancer cells is called chemotherapy. Chemotherapy for esophageal cancer can be used before surgery called neoadjuvant chemotherapy, or after surgery called adjuvant chemotherapy. In people with advanced cancer, chemotherapy can be combined with radiation therapy. However, if the esophageal cancers have spread beyond the esophagus, chemotherapy may be used alone to help relieve signs and symptoms caused by cancer.
Radiation therapy uses high-powered X-ray beams to kill cancer cells. Radiation typically can be from a machine outside the body that aims the beams at cancer called external beam radiation. Radiation therapy can also be placed inside the body, near cancer called brachytherapy. Radiation therapy is typically used before surgery, or occasionally after surgery and is also used to relieve complications of advanced esophageal cancer. Treatment can last from two to six weeks of daily radiation treatments. Side effects of radiation to the esophagus include sunburn-like skin reactions, painful or difficult swallowing, and accidental damage to nearby organs, such as the lungs and heart.
Schedule an Appointment with Our Atlanta-Area Gastroenterologists
"*" indicates required fields

